Are you tired of the same old couscous dishes in Moroccan cuisine? Well, get ready to embark on a culinary adventure as we delve into the world of Moroccan grains beyond couscous.
In this article, we will take you on a journey through the diverse and nutritious grains that are an integral part of Moroccan cooking.
From barley to quinoa, millet to buckwheat, and amaranth to many more, Morocco boasts a rich variety of grains that offer unique flavors and textures to elevate your dining experience.
Each grain has its own nutritional profile, making them not only delicious but also incredibly healthy additions to your meals.
Whether you’re looking for alternative options due to dietary restrictions or simply seeking new tastes and textures, exploring these lesser-known grains will open up a whole new world of culinary possibilities.
So join us as we go beyond couscous and uncover the hidden gems of Moroccan cuisine. Learn about the versatility of barley, discover the ancient grain quinoa in Moroccan dishes, dive into the forgotten grain of millet, unveil the secret grain buckwheat has been hiding all along, and explore the superfood properties of amaranth.
Get ready for a tantalizing journey through Morocco’s diverse range of grains that will surely leave your taste buds craving for more.
Key Takeaways
- Moroccan cuisine offers a diverse range of grains beyond couscous, including barley, quinoa, and millet.
- Barley is a versatile and nutritious grain in Moroccan cuisine, rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals.
- Quinoa, an ancient grain from South America, has made its way into Moroccan cuisine and is packed with essential nutrients and plant-based protein.
- Exploring lesser-known grains like barley, quinoa, and millet can open up new culinary possibilities and enhance the dining experience.
Barley: A Nutritious and Versatile Grain in Moroccan Cuisine
Barley is not only a delicious and versatile grain in Moroccan cuisine, but it also offers a multitude of health benefits. Barley cultivation has a long history in Morocco, dating back centuries. It thrives in the country’s diverse climate and is grown in various regions, from the coastal plains to the high Atlas Mountains.
The traditional methods of cultivating barley have been passed down through generations, ensuring its availability for use in Moroccan dishes. Barley plays a significant role in many traditional Moroccan dishes. One popular dish that showcases this grain is called ‘Hssoua,’ a hearty soup made with barley, vegetables, and meat such as lamb or chicken. The nutty flavor and chewy texture of barley add depth to the soup while providing essential nutrients like fiber, vitamins, and minerals.
Another famous dish where barley takes center stage is ‘Tfaya,’ a sweet and savory couscous dish topped with caramelized onions, raisins, and almonds. The addition of barley not only adds complexity to the flavors but also contributes to its nutritional value.
In addition to its versatility in traditional recipes, barley is known for its numerous health benefits. This ancient grain is an excellent source of dietary fiber, which aids digestion and promotes satiety. It also contains important vitamins like vitamin B6 and minerals such as magnesium and phosphorus that contribute to overall well-being.
Furthermore, barley has been linked to reducing cholesterol levels and improving heart health due to its high content of beta-glucans – soluble fibers that help lower LDL (bad) cholesterol.
As we transition into exploring quinoa’s role in Moroccan cuisine, it’s important to recognize how barley has played a significant part in shaping the country’s culinary traditions. Its cultivation practices have sustained generations of Moroccans, making it an integral ingredient in many beloved dishes. However, alongside cultural evolution comes curiosity about new grains like quinoa that offer unique flavors and nutritional profiles without forgetting the rich heritage of Moroccan cuisine.
Quinoa: Exploring the Ancient Grain in Moroccan Cuisine
Quinoa, an ancient grain that originated in the Andean region of South America, has made its way into Moroccan cuisine with a unique twist. It’s packed with health benefits and has a high nutritional profile. Quinoa is a versatile ingredient that adds depth and flavor to traditional Moroccan dishes.
From quinoa tabbouleh to quinoa-stuffed bell peppers, there are plenty of exciting recipes that incorporate this nutritious grain while still embracing the vibrant flavors of Moroccan cuisine.
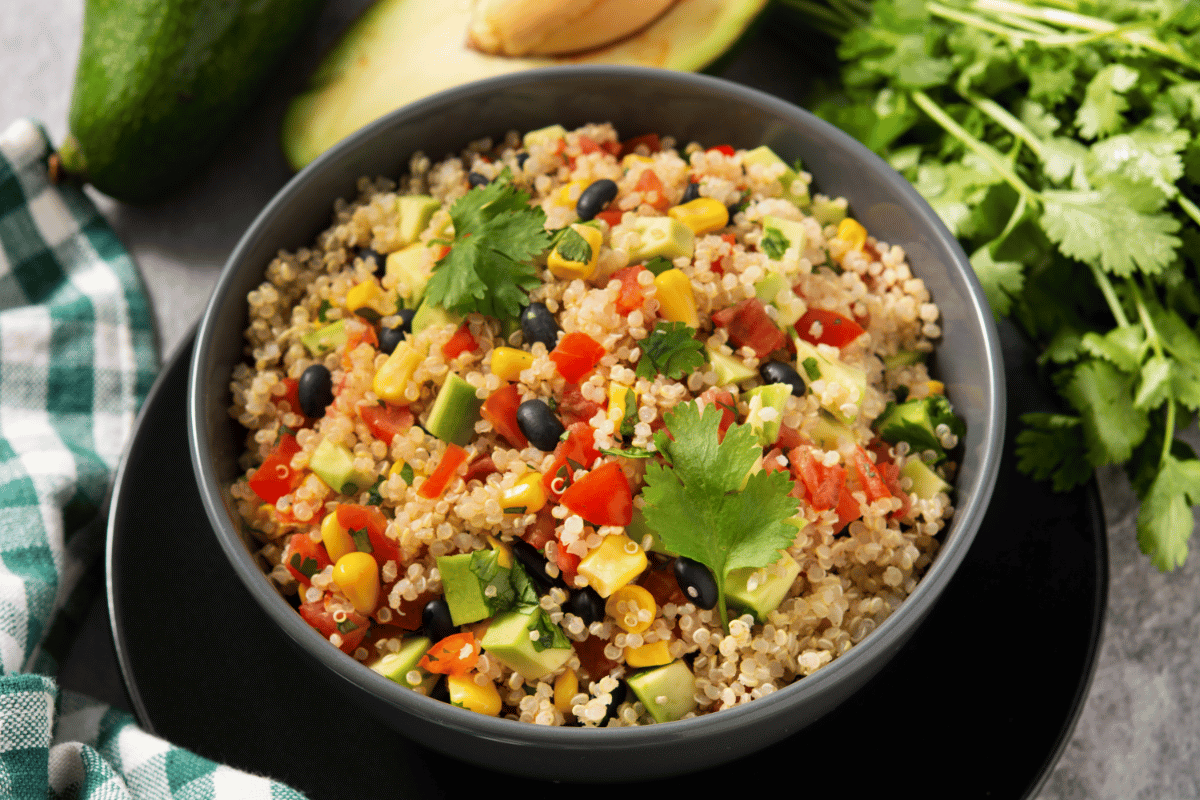

Introduction to Quinoa and Its Origins
With its origins in the Andean region of South America, quinoa has gained popularity as a nutritious and versatile grain. Quinoa farming techniques have been passed down from generation to generation, making it an integral part of sustainable agriculture in the region. The cultivation of quinoa involves unique practices such as rotating crops and using natural fertilizers, which help maintain soil fertility and prevent erosion. This not only supports the long-term viability of quinoa farming but also contributes to overall environmental sustainability.
To further emphasize the importance of quinoa in sustainable agriculture, let’s take a look at a table that showcases its positive impact:
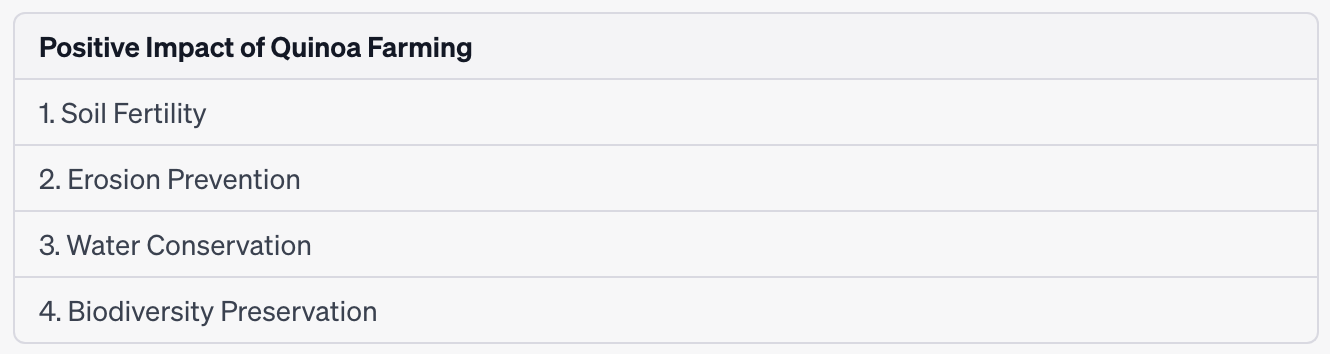
As you can see, quinoa farming goes beyond just providing a nutritious grain; it plays a vital role in maintaining the health and balance of ecosystems. Now, let’s delve into the health benefits and nutritional profile of quinoa without skipping a beat.
Health Benefits and Nutritional Profile of Quinoa
Let’s dive into the health benefits and nutritional profile of quinoa, so you can see why it’s a great addition to your diet. Quinoa is often hailed as a superfood due to its numerous health benefits.
It is packed with essential nutrients such as protein, fiber, vitamins, and minerals. In fact, quinoa contains all nine essential amino acids, making it a complete source of plant-based protein. This makes it an excellent choice for vegetarians or those looking to increase their protein intake.
Quinoa is also rich in dietary fiber, which aids in digestion and helps maintain a healthy weight. Additionally, it has a low glycemic index, meaning it doesn’t cause spikes in blood sugar levels like other grains do. This makes quinoa a suitable option for individuals with diabetes or those looking to manage their blood sugar levels.
Incorporating quinoa into your diet offers various culinary uses as well. Its mild nutty flavor and fluffy texture make it incredibly versatile in both sweet and savory dishes. You can use quinoa as a substitute for rice or pasta in salads, stir-fries, or even as a stuffing for vegetables. Its versatility extends to breakfast options too – try adding cooked quinoa to smoothies or using it as the base for porridge.
Now that we’ve explored the health benefits and culinary uses of quinoa, let’s move on to discovering delicious quinoa recipes with Moroccan flair!
Quinoa Recipes with Moroccan Flair
Immerse yourself in the rich flavors of Morocco with these delicious quinoa recipes that’ll transport your taste buds to a vibrant culinary paradise. Quinoa, combined with traditional Moroccan spices, creates a fusion of flavors that’s both unique and satisfying.
Whether you’re looking for a quick and easy meal or something more elaborate, these quinoa-based dishes are sure to impress.
- Quinoa Tabouleh: This refreshing salad combines cooked quinoa with chopped tomatoes, cucumbers, parsley, mint, and lemon juice. The addition of Moroccan spices like cumin and paprika adds a fragrant twist to this classic dish.
- Quinoa Tagine: A modern twist on the traditional Moroccan tagines, this recipe replaces couscous with cooked quinoa for a lighter and gluten-free alternative. The quinoa absorbs all the flavors from the aromatic spices like turmeric, cinnamon, and ginger resulting in a hearty and flavorful one-pot meal.
- Quinoa Stuffed Peppers: Roasted bell peppers filled with a mixture of cooked quinoa, diced vegetables such as zucchini and carrots, along with Moroccan spices like coriander and saffron create a colorful and nutritious dish that’s bursting with flavor.
- Quinoa Pilaf: This simple yet satisfying dish combines fluffy cooked quinoa with sautéed onions, garlic, toasted almonds or pine nuts for added crunchiness. Seasoned with traditional Moroccan spices like ras el hanout or baharat blends, this pilaf can be enjoyed as a side dish or as a light main course.
- Quinoa Soup: Warm up your soul on chilly evenings with this comforting soup made by simmering cooked quinoa in vegetable broth along with an array of vegetables such as carrots, celery, potatoes, and onions. Spices like cumin and paprika add depth to the soup’s flavor profile.
Transitioning into the subsequent section about “millet: discovering the forgotten grain of Moroccan cuisine,”we explore another grain that’s been a staple in Moroccan cooking for centuries.
Millet: Discovering the Forgotten Grain of Moroccan Cuisine
Millet, a forgotten grain of Moroccan cuisine, is an incredibly versatile ingredient with a rich culinary history. It not only adds a unique texture and flavor to dishes but also offers numerous health benefits. Millet is packed with nutrients like fiber, protein, and antioxidants. It is known for its ability to support digestion, promote heart health, and boost energy levels. Traditional Moroccan dishes showcase the diverse uses of millet in their cuisine, from hearty soups to comforting porridges.

Introduction to Millet and Its Culinary Uses
Although often overlooked, millet offers a wide array of culinary possibilities that are worth exploring. Millet is a versatile grain that can be used in a variety of recipes to add depth and texture to your dishes.
From pilafs and salads to porridges and baked goods, there is no shortage of millet recipes to try. One popular way to enjoy millet is by cooking it like rice and serving it as a side dish or base for stir-fries and stews. Its mild, nutty flavor pairs well with both savory and sweet ingredients, making it a great addition to both main courses and desserts.
When it comes to health benefits, millet has much to offer. This gluten-free grain is rich in nutrients such as magnesium, phosphorus, copper, and manganese. It’s also high in fiber, which aids digestion and helps maintain healthy cholesterol levels. Additionally, millet contains antioxidants that can help protect against oxidative stress and inflammation in the body. With its low glycemic index, millet can also be beneficial for those managing blood sugar levels.
So not only does millet add a delicious twist to your meals, but it also provides numerous health benefits.
Moving on from the culinary uses of millet, let’s delve into the health benefits and nutritional value of this incredible grain without skipping a beat.
Health Benefits and Nutritional Value of Millet
With its impressive nutritional profile and numerous health benefits, millet truly stands out as a valuable addition to any diet. This ancient grain is rich in nutrients such as magnesium, phosphorus, and manganese, which are essential for maintaining healthy bones and teeth. It’s also a great source of fiber, making it beneficial for digestion and promoting feelings of fullness.
Additionally, millet is gluten-free, making it a suitable option for individuals with gluten sensitivities or celiac disease.
In terms of cooking methods, millet can be prepared in various ways to suit different tastes and preferences. It can be boiled like rice or used as a base for salads and pilafs. Millet flour can be used to make breads, muffins, and other baked goods. Its mild flavor allows it to easily absorb the flavors of other ingredients, making it versatile in both sweet and savory dishes.
Whether you choose to enjoy millet as a side dish or incorporate it into your favorite recipes, its health benefits and adaptability make it an excellent choice for those looking to diversify their grain options.
Transition: Now that you understand the health benefits and versatility of millet, let’s explore how this nutritious grain is traditionally used in Moroccan cuisine with some delicious recipes featuring millet as the star ingredient.
Traditional Moroccan Dishes with Millet
Let’s delve into the rich culinary traditions of Morocco and discover how this nutritious grain takes center stage in some mouthwatering dishes.
Traditional Moroccan cuisine is known for its bold flavors and unique combinations, and millet plays a significant role in many traditional dishes.
One such dish is called ‘Harcha,’ which is a type of flatbread made with millet flour. It has a dense yet crumbly texture and is often served for breakfast or as an accompaniment to savory stews and tagines. The nutty flavor of millet adds depth to the bread, making it a delicious and wholesome option.
Another traditional Moroccan dish that incorporates millet is ‘Rfissa.’ This hearty stew features chicken, lentils, onions, and spices cooked together with millet grains. The slow cooking process allows the flavors to meld together, resulting in a comforting and flavorful dish. Millet not only enhances the taste but also provides added nutritional benefits such as fiber, protein, and essential minerals.
Incorporating millet into your diet can bring numerous benefits to your health. It’s gluten-free, making it an excellent alternative for those with gluten sensitivities or celiac disease. Millet is also rich in antioxidants that help protect against chronic diseases like heart disease and certain types of cancer. Additionally, its high fiber content aids digestion and promotes satiety, making it an ideal choice for weight management.
Now let’s move on to the next section about ‘buckwheat: unveiling the secret grain of Moroccan cuisine’ without missing a beat.

Buckwheat: Unveiling the Secret Grain of Moroccan Cuisine
You may not believe it, but buckwheat is the hidden gem of Moroccan cuisine. This versatile grain has been an integral part of Moroccan agriculture for centuries and plays a crucial role in the country’s farming techniques.
Buckwheat farming techniques have been passed down through generations, ensuring that this nutritious grain continues to thrive in Morocco. Buckwheat’s role in Moroccan agriculture goes beyond its culinary uses. It is a hardy crop that can withstand harsh climates and poor soil conditions, making it an ideal choice for farmers in remote areas. The plant itself has a short growing season, allowing farmers to cultivate multiple crops throughout the year. This not only ensures food security but also provides economic stability for many rural communities.
In Moroccan cuisine, buckwheat is used in a variety of dishes, ranging from savory to sweet. One popular dish is ‘Tfundek,’ a traditional buckwheat pancake that’s often served with honey or butter. The nutty flavor of buckwheat adds depth to these dishes, creating a unique and delicious dining experience.
Transitioning into the subsequent section about amaranth: the superfood grain of Morocco, it’s important to note that while buckwheat holds its own as a staple grain in Moroccan cuisine, it isn’t the only superfood grain worth exploring. Amaranth, another ancient grain with incredible nutritional benefits, also takes center stage in Moroccan cooking.
Amaranth: The Superfood Grain of Morocco
Now that you’ve uncovered the hidden gem of Moroccan cuisine, buckwheat, get ready to delve into another extraordinary grain: amaranth. This superfood grain holds a special place in Moroccan cooking, offering a plethora of health benefits and a unique flavor profile.
From its vibrant red hue to its nutty taste, amaranth is sure to captivate your taste buds and nourish your body.
Amaranth is not only celebrated for its distinctive qualities but also for its remarkable nutritional value. Packed with essential vitamins and minerals like iron, magnesium, and calcium, this grain provides a substantial boost to your overall well-being. Its high protein content makes it an excellent choice for vegetarians and vegans looking for plant-based sources of protein. Additionally, amaranth contains powerful antioxidants that help fight inflammation and support heart health.
When it comes to cooking techniques, there are several ways to incorporate amaranth into your culinary repertoire. One popular method is boiling the grain until it becomes tender and fluffy, similar to couscous or quinoa. This versatile base can then be used as a foundation for salads or mixed with vegetables for a wholesome side dish.
But why stop at just boiling? Amaranth’s versatility extends beyond the pot. Toasting the grains before cooking adds an extra layer of depth to their flavor profile while giving them a satisfying crunch. You can use toasted amaranth as a topping for yogurt or sprinkle it over roasted vegetables for added texture.
Incorporating amaranth into your meals not only introduces you to new flavors but also brings forth an array of superfood benefits. So why not experiment with this nutrient-packed grain? Try boiling or toasting it in various dishes and discover how this tiny yet mighty ingredient can elevate your culinary experience while nourishing your body from within.

Frequently Asked Questions
How can I incorporate barley into my everyday meals?
Incorporate barley into your everyday meals by trying out delicious barley-based soup recipes. Not only does it add a unique nutty flavor and texture, but it also provides numerous benefits for those following a gluten-free diet.
Is quinoa a traditional ingredient in Moroccan cuisine?
No, quinoa is not a traditional ingredient in Moroccan cuisine. However, it can be used as a substitute for couscous, adding a unique texture and flavor to dishes. Traditional grains like barley and millet are commonly used in Moroccan cuisine.
What are the health benefits of millet and how can I use it in Moroccan dishes?
Millet provides numerous health benefits, including high fiber content and a good source of protein. In Moroccan cuisine, you can use millet in dishes like millet pilaf or as a substitute for couscous in salads.
How does buckwheat differ from other grains commonly used in Moroccan cuisine?
Buckwheat differs from couscous in Moroccan cuisine due to its nutritional benefits. While couscous is a grain made from durum wheat, buckwheat is a gluten-free seed rich in fiber, protein, and minerals like magnesium and manganese.
What are some creative ways to incorporate amaranth into Moroccan recipes?
To incorporate amaranth into Moroccan recipes, try these creative ideas: make a traditional Moroccan salad with cooked amaranth, add it to tagines for added texture and nutrition, or use it as a base for a unique twist on couscous.
Conclusion
As you journey through the diverse grains of Moroccan cuisine, you realize that each grain holds its own unique story and symbolism. Barley, with its nutritious qualities and versatility, represents resilience and adaptability in the face of challenges.
Quinoa, the ancient grain embraced by Moroccan cuisine, symbolizes a connection to the past and a celebration of tradition.
Millet, once forgotten but now rediscovered, serves as a reminder that there is always something new to discover and appreciate in our culinary world.
And buckwheat, with its secret qualities waiting to be unveiled, captivates our curiosity and encourages us to explore beyond what we know.
Finally, amaranth stands tall as the superfood grain of Morocco, representing strength and vitality.
Just like these grains embody different qualities and meanings in Moroccan cuisine, they also represent the rich tapestry of flavors and traditions found within this vibrant country.
By exploring beyond couscous and embracing these diverse grains, we open ourselves up to a world of possibilities – both in terms of taste experiences and cultural understanding.
So next time you find yourself sitting down for a Moroccan feast or browsing through your pantry for inspiration, remember the symbolism behind each grain. Let them guide you on a flavorful journey that goes beyond mere sustenance – one that celebrates diversity, resilience, curiosity, strength, and tradition.
Embrace the grains of Morocco as more than just ingredients; let them become symbols of connection to a culture deeply rooted in history yet constantly evolving.

The Editorial Team is a passionate group of Morocco enthusiasts dedicated to sharing the beauty, culture, and wonders of this captivating country. With diverse backgrounds and a deep love for travel, we strive to bring you engaging and informative content that inspires your Moroccan adventures. From uncovering hidden gems and sharing local insights to exploring mouthwatering cuisine and showcasing the vibrant lifestyle, our team is committed to providing you with valuable resources and exciting stories that enhance your exploration of Morocco. Join us on this journey as we celebrate the rich heritage and unforgettable experiences that make Morocco truly special.




