In Morocco, Islamic customs shape societal norms, guiding behaviors with Salah prayer rituals performed five times daily. The Adhan call to prayer echoes through the streets, marking prayer times and reflecting deep religious influence. Businesses and public spaces accommodate prayer needs, emphasizing the importance of Islamic practices in daily life. Mosque architecture showcases intricate Arabesque patterns and vibrant Zellige tiles, symbolizing Morocco's cultural heritage. Festivals like Eid al-Fitr and Mawlid celebrate religious occasions, fostering community bonds. Sufism, with its mystical traditions, offers unique spiritual practices for connecting with the divine. Discover more about Morocco's rich religious traditions.
Key Takeaways
- Salah (prayer) performed five times a day is a key religious practice in Morocco.
- Adhan, the call to prayer, resounds through the streets signaling prayer times.
- Observance of Islamic festivals like Eid al-Fitr and Mawlid strengthens community bonds.
- Sufism, with practices like dhikr and meditation, offers a mystical approach to spirituality.
- Mosque architecture in Morocco reflects the country's cultural heritage and religious influence.
Islam: The Dominant Religion
Islam serves as the predominant religion in Morocco, shaping various aspects of daily life and cultural practices. Islamic customs play a significant role in regulating societal norms and behaviors. One of the most essential Islamic customs in Morocco is the practice of prayer rituals. These rituals aren't only acts of worship but also serve as a way to connect with the divine and foster a sense of community among Muslims.
Prayer rituals, known as Salah, are performed five times a day facing the Kaaba in Mecca. The call to prayer, or Adhan, echoes through the streets, signaling the time for Muslims to pause their activities and engage in prayer. This practice is deeply ingrained in Moroccan society, with many businesses and public spaces accommodating the need for prayer.
The observance of Islamic customs, including prayer rituals, reflects the strong influence of religion on the daily lives of Moroccans. Through these practices, individuals adhere to the teachings of Islam and maintain a sense of spiritual discipline and connection to the divine.
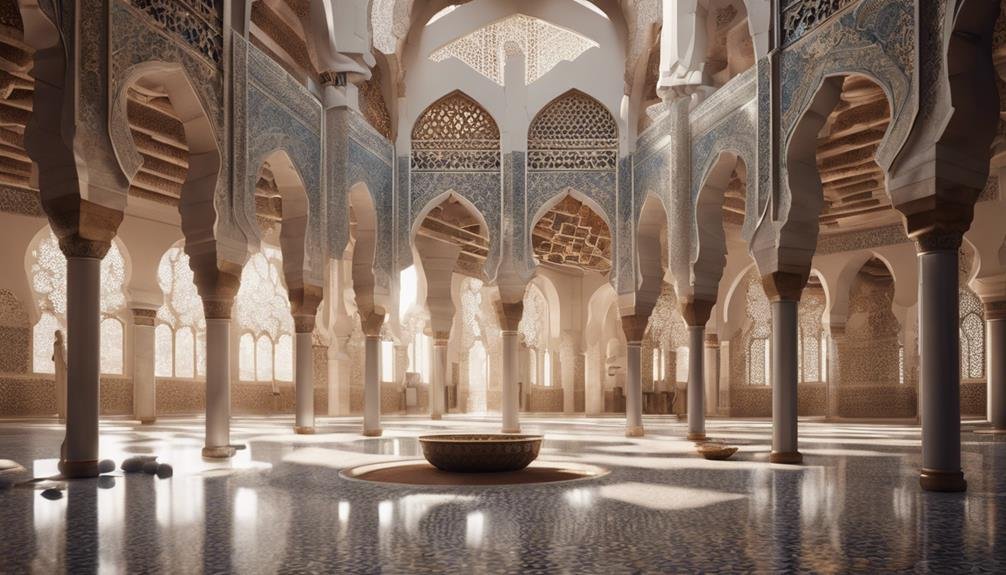
Mosque Architecture and Design
In the domain of architectural design, mosque structures in Morocco showcase a fusion of diverse influences that reflect the country's rich history and cultural heritage. Moroccan mosque architecture is characterized by intricate details and unique features that hold deep cultural significance.
Some architectural elements and design aspects you may observe include:
- Arabesque Patterns: Intricate geometric and floral designs adorn the walls and ceilings, symbolizing the infinite nature of God.
- Minarets: Tall towers from which the call to prayer is traditionally made, serving as a visual symbol of Islam in the cityscape.
- Courtyards: Often featuring central fountains for ritual ablutions before prayer, creating a serene and cleansing atmosphere.
- Use of Zellige: Traditional mosaic tilework that adds vibrant colors and patterns to the interior and exterior of mosques, representing unity and harmony within diversity.
These architectural elements blend together to create mosques that not only serve as places of worship but also as architectural masterpieces that reflect Morocco's artistic and cultural heritage.
Call to Prayer: Adhan
The Adhan, an integral component of daily religious practice in Morocco, serves as a melodic reminder to the faithful of the appointed times for communal prayer. This beautiful Islamic tradition is deeply ingrained in the daily lives of Moroccans, signaling the five prayer times throughout the day. The call to prayer, recited by a muezzin, is a poignant symbol of unity among Muslims, inviting them to engage in prayer rituals and connect with the divine.
To give you a better understanding of the Adhan, let's explore its components in the table below:
| Adhan Component | Meaning |
|---|---|
| 1. Allahu Akbar | Allah is the Greatest |
| 2. Ashhadu an la ilaha illa Allah | I bear witness that there is no god but Allah |
| 3. Ashhadu anna Muhammadar rasul Allah | I bear witness that Muhammad is the Messenger of Allah |
The Adhan not only serves as a call to prayer but also symbolizes the deep-rooted Islamic traditions and the importance of prayer rituals in Moroccan society.
Islamic Festivals and Celebrations
During various times of the year, Moroccan society engages in vibrant celebrations and festivals that reflect the rich cultural tapestry intertwined with religious significance. Two prominent Islamic festivals celebrated in Morocco are Eid al-Fitr and Mawlid. These festivals hold great importance in the Moroccan Muslim community and are marked with various traditional practices and festivities.
- Eid al-Fitr: This joyous festival marks the end of Ramadan, the holy month of fasting. It's a time for prayers, feasting, giving to charity (Zakat al-Fitr), and exchanging gifts among family and friends.
- Mawlid Celebrations: Moroccans celebrate the birth of the Prophet Muhammad during the month of Rabi' al-awwal. The celebrations include processions, recitations of poetry, and charitable activities.
These festivals not only serve as religious observances but also foster a sense of community and strengthen familial bonds. Through these celebrations, Moroccans express their devotion to Islam and honor the teachings of the Prophet Muhammad.
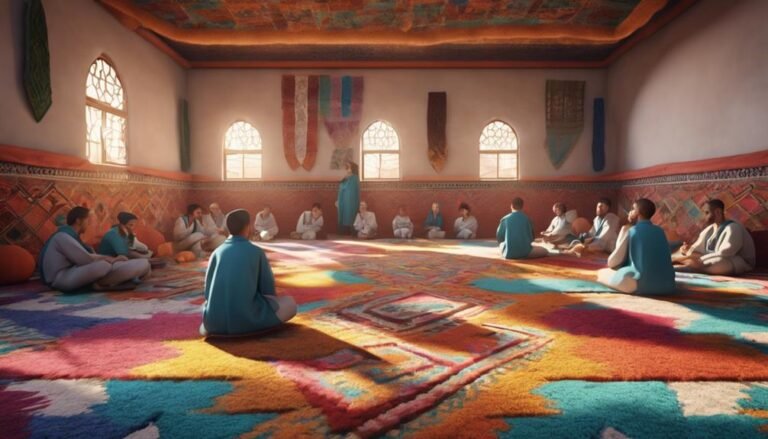
Sufism: Mystical Traditions
Rooted in the spiritual landscape of Morocco, Sufism encompasses mystical traditions that explore the depths of Islamic spirituality. Sufi rituals play a central role in the practice of Sufism in Morocco, offering adherents a way to connect with the divine on a personal and intimate level. These rituals often include practices such as dhikr (remembrance of God), meditation, chanting of sacred texts, and trance-like whirling dances known as Sufi whirling. Through these rituals, Sufis seek to achieve spiritual purification, enlightenment, and a closer relationship with God.
Spiritual practices within Sufism emphasize the inward search for God and the cultivation of the heart. Sufis in Morocco engage in practices like self-discipline, selflessness, and devotion to their spiritual guides, known as Sufi masters or sheikhs. These practices aim to help individuals transcend their ego, purify their intentions, and develop a deep sense of inner peace and connection with the divine. Sufism in Morocco continues to be a vibrant and integral part of the country's religious landscape, offering a unique perspective on Islamic spirituality.
Conclusion
To sum up, the religious practices in Morocco are deeply rooted in Islam, shaping every aspect of daily life for its people. The intricate mosque architecture, melodious call to prayer, and vibrant Islamic festivals all contribute to the rich tapestry of religious traditions in the country.
Sufism, with its mystical teachings and practices, adds a layer of spiritual depth to the religious landscape of Morocco, making it a fascinating destination for those interested in exploring the diverse world of Islam.

The Editorial Team is a passionate group of Morocco enthusiasts dedicated to sharing the beauty, culture, and wonders of this captivating country. With diverse backgrounds and a deep love for travel, we strive to bring you engaging and informative content that inspires your Moroccan adventures. From uncovering hidden gems and sharing local insights to exploring mouthwatering cuisine and showcasing the vibrant lifestyle, our team is committed to providing you with valuable resources and exciting stories that enhance your exploration of Morocco. Join us on this journey as we celebrate the rich heritage and unforgettable experiences that make Morocco truly special.