The impact of Arab-Islamic civilization on Morocco has been profound and far-reaching. From the Arabic language and culture to architectural transformation, centers of learning, and cultural exchange, Morocco has been heavily influenced by its Arab-Islamic heritage.
This article will explore the various ways in which this civilization has shaped and molded the country over the centuries.
Firstly, it is important to acknowledge the significant influence of the Arabic language and culture on Morocco. The introduction of Arabic as the official language has not only unified the nation but also facilitated communication and integration with other Arab countries. Additionally, Moroccan society has adopted numerous cultural practices, such as traditional clothing styles, cuisine, music, and art forms that are deeply rooted in Arab traditions. These cultural exchanges have enriched Moroccan identity and created a unique fusion between Arabian heritage and local customs.
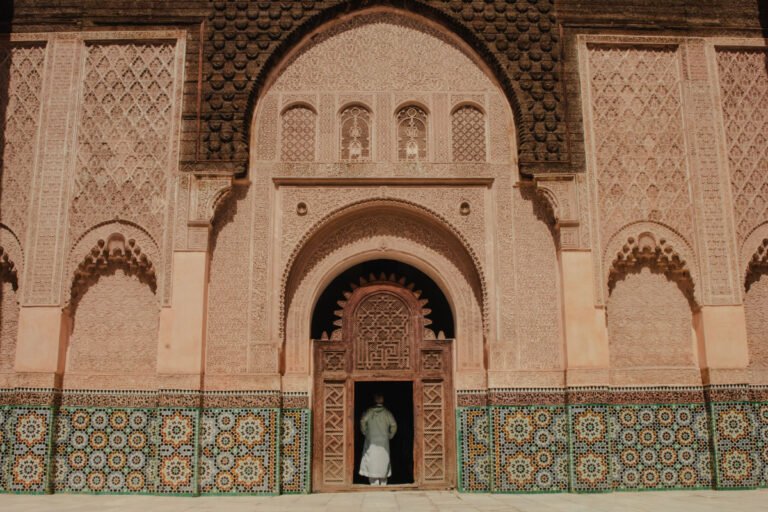
Furthermore, the architectural transformation brought about by Arab-Islamic civilization cannot be understated. The intricate geometric patterns adorning mosques and palaces across Morocco reflect an amalgamation of Islamic artistic styles from different regions. The construction techniques introduced by Arab architects have left an indelible mark on Moroccan architecture, with iconic structures like the Koutoubia Mosque in Marrakech standing as testaments to their craftsmanship. The blending of Moorish influences with local Berber designs has resulted in a distinctive architectural landscape that sets Morocco apart from its neighbors.
In conclusion, the influence of Arab-Islamic civilization on Morocco can be observed in various aspects ranging from language and culture to architecture. By embracing these influences while preserving their own unique traditions, Moroccans have created a rich tapestry that showcases their historical ties to Arabia while maintaining their own distinct identity.
Understanding this impact is crucial for appreciating both Morocco’s contributions to Islamic civilization as well as its vibrant mosaic of cultures today.
Key Takeaways
- The Arabic language and culture heavily influence Morocco.
- Moroccan architecture reflects Islamic artistic styles and techniques introduced by Arab architects.
- Moroccan cuisine has been influenced by Arab-Islamic culture.
- The impact of Arab-Islamic civilization can be seen in various aspects of modern-day Moroccan society.
Influence of Arabic Language and Culture
The aroma of Arabic spices filled the air as the rhythmic sounds of traditional music echoed through the bustling Moroccan streets, a testament to the profound influence of Arab-Islamic civilization on Morocco.
One key aspect of this impact is seen in the preservation and widespread usage of the Arabic language. The Arabic language has not only been preserved in its classical form but has also become an integral part of everyday communication for Moroccans. This linguistic assimilation can be observed in schools, media, government institutions, and various other aspects of Moroccan society.
The preservation and promotion of the Arabic language in Morocco can be attributed to its historical ties with Arab-Islamic civilization. The country’s long history as a center for trade and cultural exchange led to the adoption and integration of Arabic into its social fabric. Today, Moroccan Arabic (Darija) is spoken by the majority while Modern Standard Arabic is used in formal settings such as education and government. This linguistic assimilation has helped foster a sense of unity among Moroccans, bridging regional differences and creating a shared cultural identity.
In addition to language preservation, cultural assimilation is another significant aspect influenced by Arab-Islamic civilization. Over centuries, Morocco has absorbed various elements from Arab culture including art, music, clothing styles, cuisine, and religious practices. Traditional Moroccan architecture also reflects this influence with its intricate geometric patterns and ornate decorations reminiscent of Islamic design principles.
This cultural assimilation has not only enriched Morocco’s heritage but also contributed to its appeal as a tourist destination. Visitors are drawn to experience the vibrant souks (markets), taste flavorful tagines (traditional stews), marvel at beautifully adorned mosques like Hassan II Mosque in Casablanca or Koutoubia Mosque in Marrakech – all testaments to the enduring impact of Arab-Islamic civilization on Morocco.
As we delve into the subsequent section about architectural transformation sparked by this influence, it becomes evident that Arab-Islamic civilization left an indelible mark on Morocco. From the intricate details of its language to the vibrant tapestry of its culture, Morocco stands as a testament to the enduring legacy of Arab-Islamic civilization in North Africa and beyond.
Architectural Transformation
Explore how the architectural landscape in Morocco was transformed through the influence of Arab-Islamic culture. The impact of Arab-Islamic civilization on Morocco can be seen in its rich and diverse architectural heritage. From majestic mosques to intricately designed palaces, these structures reflect the fusion of Arab and Islamic influences with local Moroccan traditions.
The architecture in Morocco underwent a significant transformation as a result of this cultural exchange, giving rise to unique styles and designs that have shaped the country’s identity.
One notable aspect of this architectural transformation is evident in the construction of mosques. These religious buildings serve as important centers for worship and community gathering. Influenced by Arab-Islamic architectural principles, Moroccan mosques showcase intricate geometric patterns, stunning mosaics, and ornate calligraphy. These features not only contribute to their aesthetic appeal but also emphasize the importance of spirituality within Islam. The design elements used in Moroccan mosques have influenced other aspects of Moroccan architecture, such as residential buildings and public spaces.
Moreover, the influence of Arab-Islamic architecture can also be seen in traditional Moroccan palaces or ‘riads.’ These grand structures served as residences for royalty and high-ranking officials throughout history. They feature beautiful courtyards with lush gardens, elaborate tile work known as zellij, and stunning arches adorned with intricate carvings. The incorporation of these elements demonstrates how Arab-Islamic architecture has influenced not only religious buildings but also secular structures associated with power and prestige.
The impact on cuisine is another aspect influenced by the architectural transformation brought about by Arab-Islamic culture. Traditional Moroccan cuisine incorporates various flavors, spices, and cooking techniques that are directly linked to this cultural exchange. For instance, tagines – a popular dish in Morocco – are named after the distinctive earthenware pots they’re cooked in. This type of pottery originated from Arabian cultures which introduced it into Morocco during their rule. Similarly, other dishes like couscous and harira soup have been heavily influenced by Arabic culinary traditions, further highlighting the deep cultural ties between architecture and cuisine.
The architectural landscape in Morocco has experienced a significant transformation as a result of the influence of Arab-Islamic culture. Mosques and palaces showcase intricate designs that reflect the fusion of Arab and Islamic influences with local Moroccan traditions. This architectural transformation has not only shaped the physical appearance of buildings but also impacted other aspects such as cuisine. The influence on cuisine is evident through dishes like tagines, couscous, and harira soup, which have strong ties to Arabic culinary traditions. As we delve into centers of learning and cultural exchange, it becomes apparent how these architectural transformations paved the way for intellectual growth in Morocco without taking another step forward.
Centers of Learning and Cultural Exchange
Immerse yourself in the vibrant atmosphere of Morocco’s centers of learning and cultural exchange, where knowledge and ideas intertwine to create a tapestry of intellectual growth. These centers played a crucial role in the cultural diffusion that took place during the Arab-Islamic civilization’s impact on Morocco. People from different backgrounds gathered here to share their knowledge, resulting in an unprecedented intellectual progress.
One notable center of learning was the University of Al Quaraouiyine in Fez. Founded in 859 CE by Fatima al-Fihri, this institution became an epicenter for scholars from across the Islamic world. It offered courses in various fields such as mathematics, astronomy, theology, and medicine. The university also housed a library containing valuable manuscripts which attracted intellectuals from far and wide. Cultural diffusion occurred as these scholars brought their own ideas and teachings to Morocco while simultaneously incorporating elements from Moroccan culture into their studies.
Another significant center was the Library of Hassan Tower in Rabat. Built during the Almohad dynasty, this library served as a hub for intellectual exchange between scholars from different regions. It housed numerous works on topics ranging from philosophy to literature, making it a prominent destination for those seeking knowledge and engaging in discussions with likeminded individuals. This cross-pollination of ideas contributed greatly to Morocco’s intellectual progress during this period.
The third example is the Ibn Yasin Institute for Islamic Studies located in Marrakech. Established by Sheikh Abdallah ibn Yasin, this institute became renowned for its focus on religious education and scholarship. Students came here not only to study Islamic theology but also to engage with other disciplines such as history, jurisprudence, linguistics, and literature. The institute fostered an environment where intellectual curiosity thrived through debates and discussions among students and visiting scholars.
These centers of learning were instrumental in shaping Morocco’s cultural landscape through cultural diffusion and fostering intellectual progress. Their contributions laid strong foundations for future advancements in various fields, including art and literature. As we move into the next section about cultural and artistic contributions, let us explore how these centers served as catalysts for creativity and innovation during the Arab-Islamic civilization’s influence on Morocco.
Cultural and Artistic Contributions
Through the dynamic interplay of ideas and creative expressions, Morocco’s centers of learning served as vibrant hubs for cultural exchange and artistic innovation. The cross-cultural influences that permeated these spaces led to a rich tapestry of artistic achievements that continue to shape Moroccan culture today.
-
Calligraphy: Arab-Islamic civilization brought with it the art of calligraphy, which quickly became an integral part of Morocco’s artistic landscape. Skilled calligraphers meticulously crafted intricate Arabic script on various mediums, such as pottery, textiles, and manuscripts. This form of artistic expression not only served practical purposes but also conveyed spiritual significance by preserving religious texts and promoting reverence for the written word.
-
Architecture: The architectural style influenced by Arab-Islamic civilization left an indelible mark on Morocco’s cities and towns. Intricate geometric patterns, ornate tilework, and towering minarets are characteristic features seen in mosques, palaces, and other structures across the country. These architectural marvels reflect the fusion of Islamic aesthetics with local traditions, resulting in unique designs that showcase the cultural synthesis fostered by Arab-Islamic civilization.
-
Music: The influence of Arab-Islamic civilization on Moroccan music can be heard in traditional genres such as Andalusian classical music and Gnawa spiritual music. Both styles incorporate elements like melismatic vocals, complex rhythms, and improvisation techniques that trace their roots back to Arab musical traditions. These musical forms continue to captivate audiences worldwide with their hypnotic melodies and profound emotional depth.
-
Literature: Arab-Islamic civilization had a profound impact on Moroccan literature through its introduction of Arabic language and literary forms. From poetry to prose, Moroccan writers drew inspiration from both local folklore and broader Islamic literary traditions. Notable works include epic poems like ‘The Poem of Antar’, which celebrates heroism in battle, as well as philosophical treatises like Ibn Rushd’s ‘The Incoherence of the Incoherence’. These literary contributions not only enriched Morocco’s cultural heritage but also influenced later generations of writers in the Arab world.
The cross-cultural influences and artistic achievements facilitated by Morocco’s centers of learning have left a lasting legacy on the country. As we explore the enduring impact of Arab-Islamic civilization, it becomes evident that these cultural exchanges laid the foundation for Morocco’s vibrant arts scene and its appreciation for diverse forms of creative expression. From calligraphy to architecture, music to literature, the contributions made during this period continue to shape Moroccan identity and serve as a testament to the enduring power of cross-cultural dialogue.
Lasting Legacy
In modern-day Morocco, the impact of Arab-Islamic civilization continues to be felt in various aspects of society.
From architecture to language and religion, the influence of this civilization can be seen all around.
Furthermore, there’s a strong appreciation and celebration of cultural diversity in Morocco, with different traditions and customs being respected and embraced by its people.
This diverse cultural heritage adds richness and depth to the country’s identity and contributes to its vibrant cultural scene.
Continued impact of Arab-Islamic civilization in modern-day Morocco
The enduring influence of Arab-Islamic civilization in modern-day Morocco can be seen in various aspects of the country’s culture. From its language and religion to its architectural styles and traditional practices, this deep-rooted impact is evident.
It is also notable to mention the economic impact of Arab-Islamic civilization in present-day Morocco. Trade has long been a cornerstone of Arab-Islamic culture, and this tradition continues to thrive in Morocco. The country serves as a gateway between Africa and Europe, making it an important hub for international commerce. The bustling markets or souks are reminiscent of ancient trade routes that once connected distant lands.
Moreover, Moroccan craftsmanship influenced by Arab-Islamic traditions remains highly valued both locally and globally.
As we transition into exploring the appreciation and celebration of cultural diversity in Morocco, it is important to acknowledge how its rich history shaped its present state.
Appreciation and celebration of cultural diversity
Imagine stepping into a vibrant tapestry of colors, sounds, and flavors, where every corner invites you to explore the beauty and diversity of Moroccan culture. In modern-day Morocco, there is an immense appreciation and celebration of cultural diversity. The impact of Arab-Islamic civilization has led to a cultural assimilation that has fostered multiculturalism and integration within this North African nation.
Morocco’s rich history and geographical location have made it a melting pot of various cultures and traditions. Over centuries, different civilizations such as the Arabs, Berbers, Romans, French, Spanish, and Jews have left their marks on Moroccan society. This amalgamation of influences can be seen in the country’s architecture, cuisine, language, music, and art. For example, the medinas (old towns) showcase intricate Moorish architecture with its characteristic arches and geometric patterns influenced by Islamic design. The famous Moroccan tagine dish incorporates both Arab spices like cumin and coriander as well as Berber cooking techniques.
To further highlight the cultural assimilation in Morocco today is the existence of multiple languages spoken throughout the country. Arabic is the official language but Amazigh (Berber) languages are also widely spoken by indigenous communities. Additionally, French remains prevalent due to Morocco’s colonial past under France. This linguistic diversity reflects not only historical influences but also showcases a commitment to multiculturalism. Moreover, festivals such as ‘Mawazine’ celebrate different musical genres ranging from traditional Gnawa music to contemporary pop performances by international artists. These events bring people together from diverse backgrounds to appreciate and enjoy various forms of artistic expression.
The Moroccan government actively promotes integration through policies that embrace cultural diversity while preserving national identity. Initiatives like mandatory teaching of Amazigh languages in schools aim to ensure inclusivity for all citizens regardless of their cultural background. Furthermore, efforts are being made to preserve historic sites representing different periods in Moroccan history as UNESCO World Heritage Sites. This demonstrates a commitment to safeguarding the country’s heritage, promoting cultural understanding, and encouraging tourism.
Morocco stands as an example of how the impact of Arab-Islamic civilization has resulted in cultural assimilation, multiculturalism, and integration. The diverse influences found in Moroccan society have shaped its architecture, cuisine, language, music, and art. Through embracing cultural diversity while preserving national identity, Morocco promotes inclusivity and fosters a sense of unity among its citizens.
Frequently Asked Questions
How did the Arab-Islamic civilization influence the economy of Morocco?
The Arab-Islamic civilization greatly influenced Morocco’s economy through its influence on trade and economic development. It brought new trading routes, advanced agricultural techniques, and a more sophisticated financial system, leading to increased prosperity in the region.
What were the major architectural styles that emerged during the transformation of Morocco under Arab-Islamic civilization?
During the transformation of Morocco under Arab-Islamic civilization, major architectural styles emerged. These contributions were monumental and had a profound influence on the economy, showcasing the grandeur and prosperity of the region.
How did the centers of learning and cultural exchange contribute to the intellectual development of Morocco?
The centers of learning and cultural exchange in Morocco played a crucial role in the intellectual development of the country. Through intellectual exchange and cultural development, these centers fostered the growth of knowledge, ideas, and artistic expression.
What were the main forms of artistic expression that emerged during the Arab-Islamic civilization in Morocco?
Forms of artistic expression in Morocco during Arab-Islamic civilization included intricate calligraphy, geometric patterns in architecture, and vibrant tilework. These cultural influences resulted in a rich and diverse artistic heritage that continues to shape Moroccan art today.
How did the lasting legacy of Arab-Islamic civilization shape the identity and traditions of modern-day Morocco?
The lasting legacy of Arab-Islamic civilization has greatly shaped the identity and traditions of modern-day Morocco. The impact on language is evident in the use of Arabic, while the influence on cuisine can be seen in the rich flavors and spices used in Moroccan dishes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the impact of Arab-Islamic civilization on Morocco can be likened to a vibrant tapestry, woven with threads of language, culture, architecture, and knowledge. This rich tapestry has left an indelible mark on the country’s identity and continues to shape its present and future.
The Arabic language, with its lyrical cadence and expressive vocabulary, serves as the foundation upon which Moroccan society is built. It acts as a bridge between generations, connecting the past with the present. The influence of Arabic culture is evident in every aspect of daily life – from traditional clothing to culinary delights – creating a sense of unity and shared heritage among Moroccans.
Moreover, the architectural transformation brought about by Arab-Islamic civilization has transformed Morocco’s landscapes into breathtaking works of art. From the majestic mosques that dot the skyline to intricate palaces adorned with colorful tiles and geometric patterns, each structure tells a story of craftsmanship and devotion. These architectural marvels not only serve as places of worship but also stand as symbols of cultural pride and beauty.
Furthermore, centers of learning such as universities and libraries have acted as hubs for intellectual exchange throughout history. They’ve nurtured scholars who’ve made significant contributions in various fields such as mathematics, astronomy, medicine, and philosophy. The pursuit of knowledge has been ingrained in Moroccan society thanks to these institutions which continue to foster curiosity and innovation today.
Lastly, Arab-Islamic civilization has enriched Moroccan culture through its artistic expressions. Intricate calligraphy adorns manuscripts while vibrant mosaics grace walls; music fills the air during festive celebrations while traditional dances captivate audiences. These creative endeavors aren’t just forms of entertainment but reflections of deep-rooted beliefs and values cherished by Moroccans.
Overall, it’s undeniable that Arab-Islamic civilization has had a profound impact on Morocco. Its influence can be seen in all aspects of life – from language to architecture to education – leaving behind a lasting legacy that continues to shape the country’s cultural identity. As Moroccans, we’re fortunate to be part of this tapestry, woven with threads of history and tradition, which connects us to a vibrant and dynamic past.

The Editorial Team is a passionate group of Morocco enthusiasts dedicated to sharing the beauty, culture, and wonders of this captivating country. With diverse backgrounds and a deep love for travel, we strive to bring you engaging and informative content that inspires your Moroccan adventures. From uncovering hidden gems and sharing local insights to exploring mouthwatering cuisine and showcasing the vibrant lifestyle, our team is committed to providing you with valuable resources and exciting stories that enhance your exploration of Morocco. Join us on this journey as we celebrate the rich heritage and unforgettable experiences that make Morocco truly special.